Moving Averages: Trend Identification & Trading Strategies
Table of Contents
What are Moving Averages?
For anyone exploring technical analysis, moving averages are an absolute must-know tool! Think of them as a way to clear away the noise in price data – like seeing through a snowstorm to get a clearer view of the underlying trend. They work by calculating the average price over a specific timeframe, say 50 or 200 days, allowing traders to filter out those short-term jitters and focus on potentially significant shifts. It’s really key for making informed decisions.
Interestingly, there’s more than one type! The simple moving average (SMA) gives equal weight to all prices within the period. But an exponential moving average (EMA) prioritizes recent data, reacting faster to new information. Smart traders often use a combination of moving averages – it’s a clever way to confirm trends and generate even more reliable trading signals.
Defining Moving Averages
Ever feel like financial markets are just too noisy? That’s where moving averages come in! Think of them as smoothing out the price data to help you spot those underlying trends – kind of like averaging your grades for a better overall picture. Whether it’s over 50 or 200 days, these calculations give valuable insights. The Simple Moving Average (SMA) is straightforward, while the Exponential Moving Average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices. Moving averages are a simple way to see if the market’s heading up or down.
Simple Explanation of Averaging Price Data
Figuring out an average price is really useful when you’re analyzing finances—it’s like taking a broader look instead of getting caught up in daily fluctuations. For example, a 5-day moving average can help reveal trends and potential opportunities to buy or sell. Simple moving averages are fantastic for spotting shifts in market momentum; they offer valuable insights that traders often rely on.
Types of Prices Used (Closing, High, Low, etc.)
Technical analysis relies on key price points to anticipate shifts in the market. Take the closing price, for instance—it reflects the final value and frequently influences daily trends. You’ll also see high and low prices, which show how much a stock fluctuates throughout the day, like its peaks and valleys. Finally, the open tells you where trading started. Understanding these distinctions is really important when reading charts.
Calculating Moving Averages
Spotting trends in the market? Calculating moving averages is a fantastic way to do just that! Think of a Simple Moving Average (SMA) as smoothing out data – for example, averaging the closing prices from the last ten days. Exponential Moving Averages (EMA) work similarly, but give more weight to recent activity. Shorter periods highlight quick shifts, while longer ones show you the bigger picture. Really mastering moving averages can significantly improve your market analysis; why not dive deeper and refine your trading approach?
Formula for Simple Moving Average (SMA)
The Simple Moving Average (SMA) is a really useful technical indicator – it takes complicated price data and makes it easier to understand. Think of it as smoothing out the bumps by averaging prices over a specific period, say 20 days. That ‘n’ in the formula—SMA = (Sum of prices) / n—represents that timeframe. This moving average can highlight potential trend shifts and important support/resistance levels, making spotting patterns much simpler for traders.
Understanding the Impact of Period Length
Figuring out period length is key to how well technical indicators work! Think about it – shorter periods jump at every price change, which can be great for quick reactions but also means more false signals. Longer periods offer a smoother view of trends, though they might lag and cause you to miss some early moves. Moving averages are a perfect example; a faster MACD setting is responsive, while a slower one helps ignore the little bumps in the road. Ultimately, selecting the right period length really depends on your trading style and what’s happening in the market.
Types of Moving Averages
Moving averages are incredibly useful for technical analysis – they help traders identify trends and potential support or resistance levels in the market. You can think of them as smoothing out price fluctuations, like making a bumpy road easier to navigate so you can see the general direction things are heading. There’s actually quite a variety of moving average types available, each suited to different trading styles; getting familiar with these differences is key to success.
Let’s look at some common ones: a Simple Moving Average (SMA) calculates the average price over a specific period. Then there’s the Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which gives more weight to recent prices, making it quicker to react to new information. Finally, the Weighted Moving Average (WMA) also emphasizes current data but uses a slightly different method for doing so. Ultimately, choosing the best moving average really comes down to your own trading strategy and what you’re hoping to achieve.
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
The Simple Moving Average (SMA) is a really useful tool for understanding financial markets. It essentially smooths out those daily price jumps and helps you spot potential trends – think of it as averaging prices over a set period, like 20 days! This gives you one clear value representing the average, cutting through some of that market ‘noise’. Shorter timeframes will react quickly to changes, while longer ones offer a more gradual, though slightly delayed, view using moving averages.
Calculation and Characteristics
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence, or MACD, offers a clever way to spot changes in momentum. Essentially, it looks at the difference between two moving averages – one tracking short-term price trends (12 days) and another focusing on the longer view (26 days). Then, it compares that result to a 9-day EMA, known as the signal line. Keep an eye out for crossovers and divergences; they can provide some really useful trading signals.
Visual Example: SMA on a Chart
Seeing a visual example really helps grasp the Simple Moving Average (SMA) – think of it like smoothing out a bumpy road to reveal the direction ahead! Calculated over a specific timeframe, such as 20 days, the SMA filters out those rapid price fluctuations. It’s true that this method does lag a bit, but it still offers valuable clues about potential support and resistance.

Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a really useful technical indicator – it helps smooth out price data so you can better spot trends. Unlike a Simple Moving Average (SMA), the EMA gives more weight to recent prices; it’s like paying closer attention to today’s news than what happened yesterday! This makes it quite responsive, letting traders react quickly to changing market conditions. Ultimately, this moving average calculation highlights current data, giving you a clearer look at short-term momentum and potential shifts in trends.
Calculation and Characteristics – Smoother than SMA?
Weighted Moving Averages (WMA) provide a clever alternative to Simple Moving Averages (SMA). Unlike the latter, moving average calculations prioritize recent data – imagine valuing today’s headlines more than those from weeks ago! This thoughtful approach leads to smoother trend spotting and quicker responses to price changes. It’s fantastic for traders wanting timely signals, though be mindful of potential increased sensitivity.
Visual Example: EMA on a Chart
Take a look at this visual example of an EMA on a price chart – you’ll notice that smooth line! It’s quite different from a Simple Moving Average because it responds rapidly to recent price movements. This quick reaction makes the EMA really useful for identifying short-term trends and potential trading opportunities. The period setting determines how sensitive it is; shorter periods mean quicker adjustments. Pretty neat, right? It adapts well to momentum shifts, giving you valuable insights into market direction. Want to learn more about moving averages? Check this out.
Weighted Moving Average (WMA)
Spotting trends in price data can be tricky, right? That’s where the Weighted Moving Average (WMA) comes in handy. Unlike a simple moving average, it gives more importance to recent prices—essentially, today’s news matters more than what happened weeks ago. This means the WMA tends to react faster and might give you an earlier heads-up about potential shifts in direction. Imagine a 10-period WMA really highlighting those latest price changes! Want to dive deeper into how moving averages work? Check out this explanation: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/w/weightedmovingaverage.asp. Why not explore using the WMA to refine your trading strategy?
Calculation and Characteristics - Giving More Weight to Recent Prices
Want to make moving averages react faster? Traders often do, giving more importance to recent prices—it’s like focusing on the latest headlines! Exponential moving averages (EMAs) are a great way to achieve this, quickly responding to price changes and minimizing lag. Keep in mind though, that increased sensitivity can sometimes mean they’re influenced by market fluctuations. Curious about different types? Check out more details here.
Visual Example: WMA on a Chart
A moving average chart provides a smoothed perspective on price data—think of it as seeing trends with a gentle focus. The Weighted Moving Average (WMA) is particularly useful; it prioritizes recent prices, allowing for quicker reactions compared to basic averages. You’ll likely notice how the WMA swiftly mirrors new highs and lows, making it easier to identify emerging patterns.
Identifying Trends with Moving Averages
Analyzing financial data can be tricky with all those price swings! Moving averages are a fantastic tool to help smooth things out – picture looking at a map instead of a bumpy road; that’s essentially what they do. They calculate an average over a specific period, like 50 or 200 days, making it easier to see the bigger trend and filter out some of the noise. You’ll find different kinds too! Simple moving averages (SMA) give equal weight to each price point, while exponential moving averages (EMA) focus more on recent data.
Interestingly, crossovers between these moving averages can offer clues. A shorter-term average crossing above a longer one might suggest an upward trend is developing, and the reverse could hint at a potential downturn. Just remember they’re lagging indicators – they show what’s already occurred, so don’t rely on them for predicting the future!
Uptrends & Downtrends
Understanding uptrends and downtrends is absolutely vital in trading – think of it as identifying hills versus valleys on a price chart! An uptrend signals optimism, with prices consistently reaching higher highs and lows. Conversely, a downtrend suggests potential selling pressure, showing lower highs and lows. Recognizing these patterns can really inform your trading strategy; many traders look to buy during those upward pushes and sell when things start heading south. Moving averages are often helpful for getting a clearer picture of these shifts.
How MAs Confirm Trend Direction
Spotting trends becomes much easier with moving averages (MAs)! Think of it like a quick runner overtaking a marathoner – when a shorter MA crosses above a longer one, that often signals an uptrend. The reverse suggests a downtrend, providing helpful clues. Don’t forget to check the slope of your moving average, too; a rising slope reinforces upward momentum.
Using Multiple MAs for Confirmation
Confirming trading signals with multiple moving averages is a smart way to boost accuracy! When shorter-period moving averages cross above longer ones, it’s often a sign of an uptrend – like catching that initial momentum. Conversely, if those lines start to diverge, it could hint at a potential reversal. Many traders find the 50-day and 200-day MAs particularly useful.
Keep in mind, these averages are best used for confirmation; don’t treat them as your only indicator. Combining this approach with other technical analysis techniques gives you a fuller picture of what’s happening in the market.
Crossovers as Signals
Moving averages can be really helpful when you’re trying to spot changes in market trends. Think of a bullish crossover – that’s when a shorter-term average climbs above a longer one, kind of like a plant reaching for the sun, and it could signal an upward trend. On the flip side, a bearish crossover, where the short-term falls below the long-term, might suggest things are heading downward. Just remember these crossovers offer signals, not certainties! Always factor them into your trading plan and look at other indicators too. Want to learn more? Explore different moving average strategies – it’s a great way to level up!
Short-Term vs. Long-Term MA Crossovers (Golden/Death Cross)
Moving average crossovers can be really helpful technical indicators to keep an eye on! You’ve probably heard of the Golden Cross – that’s when a shorter-term average, like the 50-day, climbs above the 200-day, and it often suggests things are looking up. On the flip side, a Death Cross, where the short-term dips below the long-term, could signal a more bearish outlook. Just remember these indicators lag a bit; pairing them with other analysis will give you a clearer picture of market trends.
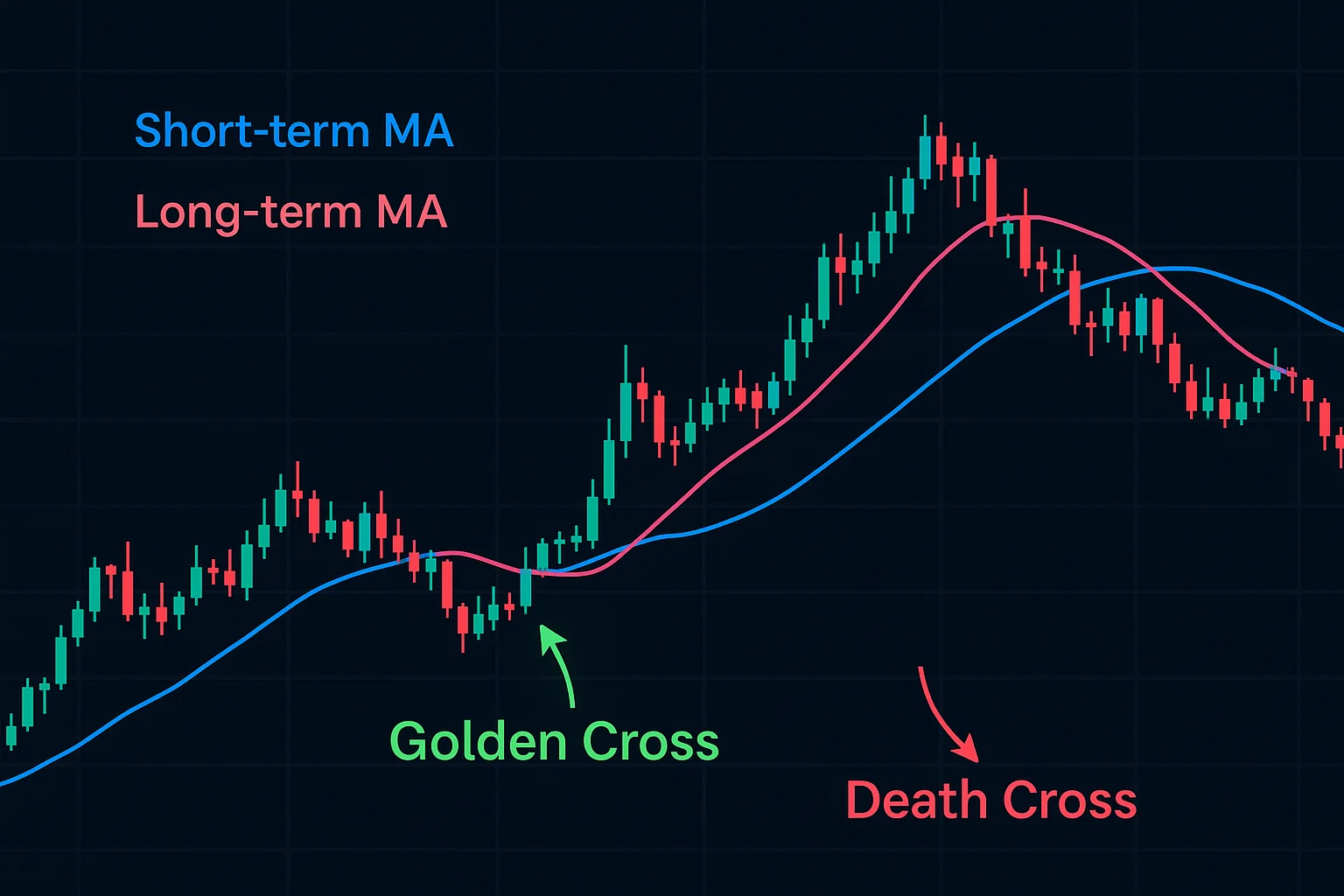
Interpreting Different Crossover Combinations
Figuring out crossover combinations is really important for smart trading! Seeing a bullish MACD crossover backed by a rising RSI? That often suggests strong momentum and a good buying opportunity. But be careful—a bearish crossover with an oversold RSI might just indicate a short-term dip before prices bounce back. Sometimes, indicators disagree – like a bullish MACD alongside a declining RSI – which could signal fading momentum.
Choosing the Right Period
Selecting the right period is key to a winning trading strategy – it’s truly vital! The moving average period you choose dramatically impacts how quickly your indicator reacts to price changes; imagine fine-tuning a camera lens. Shorter periods, like a 10-day MA, are quite responsive and fantastic for short-term traders seeking quick signals. On the other hand, longer periods—the 200-day MA is a popular example—provide a broader perspective on long-term trends, perfect for investors with a buy-and-hold approach.
Ultimately, your trading style should be your guide here. And remember volatility! When markets are choppy, longer periods can help filter out the noise and prevent false signals. Truly understanding how different moving average periods behave in various situations is essential for maximizing potential profits.
Factors Influencing MA Period Selection
Finding the perfect moving average period can really help you identify those key trends! Imagine it like this: shorter periods, say 10 days, react quickly to price changes—lots of signals there, but some might be false alarms. On the other hand, longer MAs, such as a 50-day or even a 200-day, offer a much smoother view and are fantastic for long-term investing. Many traders tweak their settings depending on how the market’s behaving and what works best for them; more volatility often means opting for a longer timeframe.
Trading Style & Timeframe Considerations (Scalping, Day Trading, Swing Trading)
Different trading styles really depend on your chosen timeframe. Think of scalping as super-fast moves – trades that last just seconds or minutes, aiming for small but regular profits. Day traders hold onto positions throughout the day, and swing traders try to catch gains over days or weeks by capitalizing on momentum.
Common MA Periods and Their Uses
Spotting market trends becomes much easier when you understand moving averages. For example, the 50-day MA offers a quick look at shorter to medium-term momentum. If you zoom out, the 100-day MA highlights longer-term movements and potential price levels. Many traders consider the 200-day MA a crucial signal for significant trends – it’s essentially viewing the bigger picture! Curious about these powerful tools? Explore our guide on technical indicators to learn more.
50-day, 100-day, 200-day MAs – What Do They Mean?
Moving averages (MAs) are really useful technical indicators – they smooth out price data to help spot trends. Think of the 50-day MA as showing you short-term momentum, kind of like a quick burst of speed. The 100-day MA gives a broader view of intermediate trends, and the longer 200-day MA? That’s your key benchmark for long-term direction! Many traders watch for crossovers – when shorter MAs cross over longer ones, it could signal an uptrend, but moving below might suggest some weakness.
Trading Strategies with Moving Averages
Many traders find moving average indicators incredibly useful for smoothing out price data and identifying trends in financial markets – it’s a core part of many strategies! A common technique is the Moving Average Crossover: you might buy when a shorter-term MA crosses above a longer one, signaling a possible uptrend, and sell when that reverses. Or, you could use moving averages to identify dynamic support and resistance levels, looking for price bounces off them. Some even employ the Multiple Moving Average approach, using several MAs with varying periods to confirm the overall trend.
Of course, no strategy is perfect. Crossovers can sometimes generate false signals, especially when markets are volatile – it’s a bit like trying to navigate through dense fog! It’s also important to remember that relying solely on moving averages ignores other crucial factors like trading volume and current news events. Ultimately, determining the ideal MA period often involves testing different assets and timeframes.
Trend Following Strategy
Ever notice how things tend to keep going in one direction for a while? That’s what trend following strategies try to capitalize on – riding those established market trends, whether prices are rising or falling. The core idea is simple: jump into a trade that’s already gaining momentum and stick with it until the signals tell you otherwise. Finding reliable trends is key, and many traders use technical indicators like moving averages to help filter out noise and confirm things are really moving. Both simple (SMAs) and exponential (EMAs) moving averages are popular tools for this. Trend following isn’t about predicting what will happen; it’s about reacting to what has already happened, aiming to profit from those sustained movements.
Identifying Trends & Entering Trades in the Direction of the Trend
Understanding market trends is vital for successful trading, right? Moving averages really help visualize price action and confirm whether things are generally heading up or down. Keep an eye out for those consistent shifts supported by volume – that’s often a solid trend forming! Bolstering your analysis with other indicators can be smart before you invest. Trading with the prevailing trend tends to maximize gains, so try not to go against it. And of course, always remember good risk management!
Using MAs to Set Stop-Loss Orders
Thinking about moving averages for stop-loss orders? It’s a really smart way to manage risk, offering more flexibility than fixed levels. A simple approach is placing stops below a shorter-period MA when you’re buying, or above when selling – it adapts well to changing market conditions. For quicker signals, consider an Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Ultimately, pick an MA that fits your trading style; slower MAs give you wider stops, which can be great for riding trends.
Crossover System
Many traders find crossover systems quite appealing – they use moving averages as a helpful guide for spotting potential opportunities. Think of it this way: when a shorter-term moving average crosses above a longer one, that often hints at an emerging upward trend. Conversely, if the short-term MA dips below the long-term, it might suggest downward momentum is building. However, remember these crossovers aren’t perfect; confirming them with other technical indicators is always wise to avoid misleading signals.
Rules for Buying and Selling Based on MA Crossovers
Want a straightforward way to spot trends? Moving Average Crossovers offer just that! Keep an eye out for a golden cross, where the 50-day average climbs above the 200-day – it might signal a good time to buy. Conversely, a death cross suggests caution. Remember to always use stop-loss orders and confirm crossovers with other indicators to avoid false alarms.
Risk Management Considerations
Achieving consistent trading success really comes down to smart risk management – it’s like laying a solid foundation for everything else! Diversification and carefully sizing your positions are essential, alongside using stop-loss orders. Don’t forget to regularly review your risk exposure and adjust accordingly; it’s about proactively protecting yourself. Sticking to your pre-defined risk tolerance, maybe with moving averages to spot trends, is also vital.
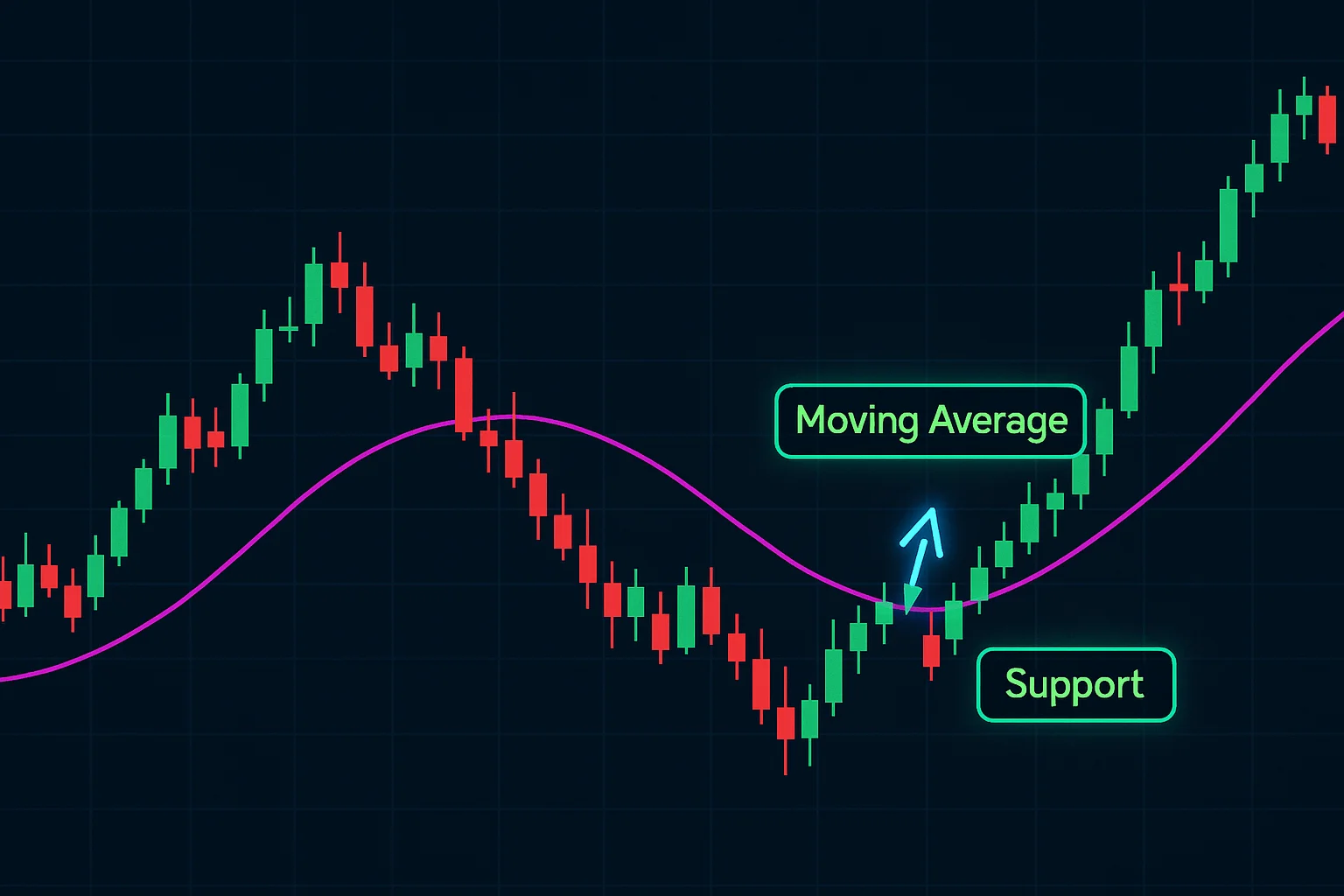
Dynamic Support and Resistance
Dynamic support and resistance levels aren’t set in stone; they shift over time, much like a river changing its course. Unlike fixed price points, these levels are often calculated using indicators—think of something like moving averages. A 50-day moving average, for example, can frequently act as dynamic support, where prices tend to bounce before continuing upward.
Keeping an eye on these dynamic levels can offer traders valuable clues about potential entry and exit points. It’s all about adapting your strategies and spotting those market trends! Want to learn more? Explore different moving average techniques today.
How MAs Can Act as Potential Support/Resistance Levels
Ever noticed how prices seem to hover around certain lines on a chart? That’s often because of moving averages (MAs)! They frequently act as dynamic support and resistance – it’s really about trader psychology at play. When price approaches a key moving average, many traders expect something to happen, which can create buying or selling pressure.
Think of them as potential turning points; prices often test these levels. A bounce suggests the level holds, while a break signals changing momentum. Understanding this helps refine your trading strategy and better spot trends using moving average indicators.
Limitations of Moving Averages
Spotting trends is easier with moving averages, but it’s good to know they have limitations. One thing to remember is that these tools always lag behind price action – kind of like looking through a rearview mirror! Because calculations rely on past data, signals tend to show up after a trend has already begun, potentially causing missed opportunities or trades made at the wrong time. It’s also worth noting that relying solely on moving averages can be risky; they’re susceptible to whipsaws during volatile market conditions.
And let’s face it, moving averages aren’t exactly crystal balls when it comes to predicting sudden changes in direction. They really shine at confirming trends already underway rather than forecasting what’s next. To build a stronger trading strategy, consider pairing them with other technical indicators and even incorporating fundamental analysis.
Lagging Indicator Nature
Lagging indicators—things like moving averages—tend to reflect what’s already occurred. They confirm trends based on past performance; it’s kind of like realizing it’s raining after you’re soaked! Since they use historical data, signals don’t appear until a trend is underway. To get a more complete view, consider combining lagging indicators with leading or coincident ones. Examining various timeframes and other factors can help refine your predictions, despite this built-in delay.
Why MAs React to Past Data, Not Future Events
Moving averages (MAs) offer a helpful way to smooth out those sometimes-wild price swings by averaging data—say, over 20 days. It’s worth remembering that because they look at past prices rather than predicting the future, there’s a bit of a delay as the moving average adjusts. Kind of like checking your rearview mirror; it gives you a sense of where you’ve already been! MAs are fantastic for identifying trends, though.
False Signals & Whipsaws
Technical analysis can be tricky – ever felt misled by false signals or whipsaws? Think of market noise like static interfering with a clear song; it obscures the underlying trend. These pitfalls, especially when using tools like moving averages, can lead to quick losses. To help avoid them, try confirming your analysis with multiple indicators and looking at broader timeframes. Understanding what’s just volatility versus a genuine shift is key! Want to dive deeper into moving averages? Check out our guide for more advanced strategies.
Dealing with Market Noise and Avoiding Premature Trades
Market noise—those flashing headlines and sudden price changes—can really throw a wrench in your trading plans, right? Seasoned traders handle this by staying focused on their established strategies and pre-set risk levels. It’s all about tuning out the distractions to keep an eye on what truly matters for consistent success.
Moving averages are helpful tools for smoothing price data and spotting those underlying trends. Try not to react impulsively to short-term bumps; instead, wait for confirmation signals that fit your plan—a proactive move like that minimizes premature trades.
Integrating MAs into a Trading Journal
Adding Moving Averages to your trading journal can really boost your progress toward more consistent results. Let’s start simple: jot down the specifics of each trade – what moving average did you use, like a 50-day or maybe a 200-day? Then record those crossover signals, both buy and sell, along with your entry and exit points and how long you held the position. But here’s the key: explain why you made that trade! Was it just the crossover itself, or part of something bigger?
Think about including a bit about what was happening in the market at the time – did other indicators back up your signal? Regularly reviewing these entries focused on Moving Averages will uncover some really valuable insights. You can analyze win rates for different combinations and spot patterns in those false signals. For instance, were there specific conditions that often led to inaccurate predictions? Use this information to tweak your strategies, adjust those MA periods, or add extra confirmation tools – consistent journaling helps you objectively see how well your MA-based approach is performing.
Tracking MA Performance
Want to really level up your MA performance? It’s all about keeping a close eye on how things are going! Regularly checking those key metrics – like conversion rates and ROI – gives you a clear picture of what’s working well. Plus, seeing how customers interact with your campaigns—whether they click, open emails, or share content—tells you exactly what resonates most.
Most marketing automation platforms have handy analytics dashboards, but connecting to tools like Google Analytics can unlock even more detailed reporting. This data is gold; it helps you spot areas for improvement and fine-tune your strategies based on real insights.
Recording Trade Entries, Exits, and Rationale
Keeping accurate records is absolutely key for trading success—it’s really like a pilot’s flight log! Jotting down when you enter and exit trades, along with the exact prices, lets you analyze your performance effectively. Don’t forget to add why you made those choices; maybe it was an indicator signal or just your read on the market – that context is invaluable.
Analyzing Results to Optimize Strategies
Seeing how your trades play out? It’s a must for anyone serious about long-term success! Regularly checking those wins and losses can reveal surprising patterns, letting you tweak your strategies based on real data—focusing on actionable insights, not just the numbers themselves. Adapting as you go, especially when using tools like moving averages, is really key to getting better over time.
Benefits of Using Tools Like Flows.Trading for Journaling
Struggling with traditional notebooks for tracking trades? Tools like Flows.Trading provide a real upgrade. Think about easily logging your trades and market observations – that’s the power of financial analysis features. Integrated charts make data visualization simple, helping you quickly identify patterns and gain valuable performance insights to inform better decisions.
Flows.Trading does more than just jot down notes; it streamlines your entire workflow. Automated data capture frees up precious time, while customizable reports give you a clear overview of your trading activity. Ready to level up your strategy? Start journaling smarter today!
Improved Strategy Validation & Backtesting
Before you put your trading plan into action, it’s really important to validate your strategy and backtest it thoroughly. Consider it like test-driving a car – you wouldn’t just drive off without checking everything! Simulating performance using historical data, factoring in costs such as slippage, is incredibly helpful. Testing across different market conditions and timeframes ensures robustness.